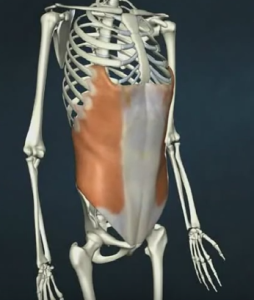
Oblique muscle strains, pulls, or other injuries are typically caused due to stress exerted by forceful movements or increased repetitive motion. Partial tears or overstretching of the muscle can also lead to incapacitating and painful oblique muscle strain.
Complete recovery of an oblique muscle strain or pull can take about 4 to 6 weeks or even more. As the muscles are crucial to many daily activities, patients need to start the treatment of strained oblique muscles at the earliest.
Symptoms of strained oblique muscle
An oblique muscle pull or strain may be accompanied by the below listed signs and symptoms:
- Oblique muscle strains or pulls are generally marked by sharp and sudden pain in the abdominal area and around the lower ribs.
- The pulling/stretching sensation or pain often gets pronounced when doing activities that use or stress the internal oblique muscles.
- Sometimes, patients may not experience any symptoms when doing activities or exercising. Pain and discomfort may however arise when the body and muscles begin cooling down.
- Oblique muscle pain can occur suddenly as a forceful blow or it may occur slowly over the course of a training session.
- Oblique muscles tend to be more proactive when sitting as compared to lying down. Hence, symptoms of muscle strain are more evident when sitting or standing.
- Bending and twisting movements can be very painful. In severe instances, intense pain may occur when coughing, breathing deeply, sneezing, or laughing.
- People with oblique muscle strain may also elicit stiffness when resting after activities, particularly when waking up in the middle of the night or in the morning.
- People with severe oblique muscle pull may suffer from muscle spasm, swelling, bruising, tenderness, and weakness.Stretching or touching the affected area, the ribs, or the abdominal sides can exacerbate the symptoms.
Causes of pulled oblique muscle
Oblique muscle strain is usually caused by sudden constriction of the internal oblique muscles when it is getting stretched. The muscles are most active and get stretched when bending sideways or forwards or during twisting motions.
Golf, baseball, and tennis are some of the sports that is associated with the condition.
Activities like throwing, bowling, rowing, heavy lifting, and side sit ups can also cause oblique muscle pull or strain.Crunches, sit-ups, and other high-intensity workouts that target the abdominal muscles can also trigger an oblique muscle strain.
Mild strain can also occur due to simple things like sneezing excessively or forcefully or chronic coughing.
Treatment of oblique muscle
An oblique muscle strain or pull takes about 10 weeks to resolve completely. Treatment involves the following:
- Oblique muscle strain can be very painful. As the recovery period is very long, patients may be able to bear such pain for such a long time. Hence, OTC painkiller medications like aspirin, ibuprofen, or other NSAIDs may be used. These drugs help alleviate inflammation, swelling, and pain.
- Apply an ice pack or cold compresses in the affected area during the first 48 to 72 hours after sustaining the pull. Ice packs decrease swelling, lowers the blood flow, and eases inflammation. Cold compresses may be used for 10 to 20 minutes at a stretch, rest for 30 minutes to an hour, and then repeat the ice therapy. Do not use ice if the skin turns pinkish or red. Do not apply ice directly on skin as it can cause burns.
- After the first 48 to 72 hours, stop using ice packs and shift to heat application. Heat compresses stimulate the flow of blood, relax the muscles, and promote healing of injured muscle tissue. Each session may last for 10 to 20 minutes. Repeat the therapy after resting the area for 30 minutes to an hour. People with diabetes and circulatory problems should not use heat therapy.
- It is important to rest the strained oblique muscles. During the recovery period, avoid all activities that may stress the muscles and worsen the injury. Keep the injured part of the torso in an elevated position to reduce swelling and hasten the healing process.
If an oblique muscle strain does not respond to the rest, ice, and heat therapeutic method, or if the pain is severe, then patients may seek medical care.
- Doctors may suggest prescription painkillers, muscle relaxants, and opioid analgesics for pain alleviation.
- Severe oblique muscle injuries may need a rehabilitation program and/or physical therapy.
- Strain or pull injuries rarely require surgical treatment. However, if the injury involves muscle tear or rupture, then doctors may recommend surgery.