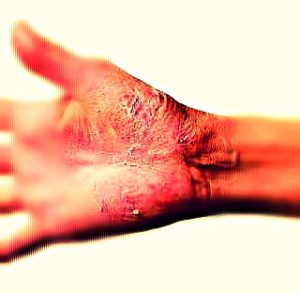
Symptoms of tinea manuum
Some common signs and symptoms of tinea manuum are listed below:
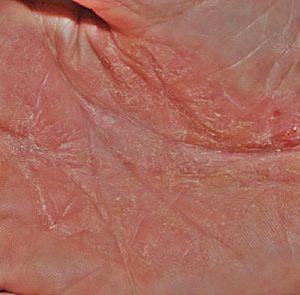
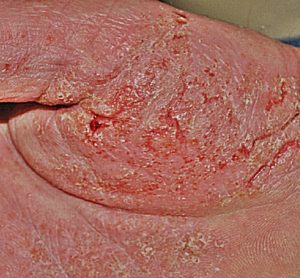
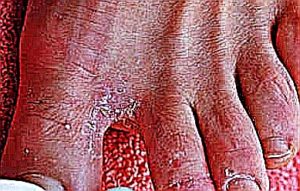
- Skin rash with elevated red borders and an almost clear center area which makes that rash look circular or like bulls-eye.
- The rash is extremely itchy and there may be burning sensations. The intensity of these symptoms may vary in different patients
- Usually one hand develops the rash. If both hands are affected by tinea manuum, then the rashes on either hand are asymmetrical.
- Dryness of skin along with skin peeling may occur
- The sides of infected fingers as well as the palm may develop groups of small blisters which often tend to discharge fluids or ooze
- Tinea manuum skin rash which heals after a prolonged presence often causes skin discoloration.
Causes of tinea manuum
The top skin layers consist of dead skin cells that are full of keratin proteins. This ensures that the skin remains waterproof, provides strength and toughness to the skin, and protects the inner fragile parts of skin and body from environmental elements.
Healthy skin generally heals rapidly. However, cuts or other anomalies that affect unhealthy skin heals slowly, which makes it prone to different kinds of infections. Such opportunistic infections are more prevalent in people with weakened immune systems.
Dermatophyte fungi cause superficial skin rash infections on skin’s outermost layer. This fungus has specific enzymes called keratinases which process and digest the proteins on skin surface and thus facilitates the growth and multiplication of the fungal infection.
The fungal infection can transmit from animals to humans, from infected human to healthy humans, and from soil to humans. Zoophilic, anthropophilic, and geophilic dermatophytes are respectively spread via the above modes of transmission.
In most cases, tinea manuum is caused due to transfer of a pre-existing fungal infection on some other area of the body to the hands. Patients may keep scratching dermatophyte skin rash on the feet or other places and this results in spread of fungus to the hands.
- Most cases of tinea manuum skin rash are caused by anthropophilic infections. A few common anthropophilic fungi known for causing tinea manuum are T.rubrum, epidermophyton floccosum, and trichophyton interdigitale.
- Trichophyton verrucosum fungi can transfer from cattle, microsporum canis from cats or dogs, and microsporum gypseum from soil.
Tinea manuum can affect anyone and everyone. However the below listed risk factors can increase the susceptibility to developing the skin rash:
- Close contact with a person infected by the fungi
- An underlying case of dermatophyte fungal infection on some other place on the body
- Presence of some other skin disease; tinea manuum may occur as a secondary infection of some other skin disease like contact dermatitis which has made the skin unhealthy and diseased and thus at increased risk to fungal and other kinds of infections.
- Increased and abnormal sweating
- Workers at farms who have regular contact with soil or livestock, especially cattle
- Frequent contact with pets; it typically causes tinea manuum in more children than adults
- Gardeners as well as manual laborers who come into regular contact with soil, especially soil contaminated with different kinds of pathogens
Treatment of tinea manuum and Home Remedies
Tinea manuum can be completely cured in about 4 to 6 weeks with the use of topical and oral antifungal medicines.
- Antifungal gels and ointments used for treating tinea manuum include clotrimazole, terbinafine, ciclopirox, butenafine, and/or econazole
- Doctors may prescribe oral antifungal capsules or tablets like fluconazole, terbinafine, griseofulvin, or itraconazole for tinea manuum treatment.
- In cases where tinea manuum has developed as a secondary infection, due to presence of some other skin disease, the pre-existing skin ailment also needs to be treated to prevent recurrence of dermatophyte skin rash.
A few home remedies for tinea manuum are as follows:
- Hydrogen peroxide can be used for cleaning different kinds of skin infections, including tinea manuum fungal infection of the hands. Mix hydrogen peroxide with water and apply on skin rash
- Apple cider vinegar and tea tree oil has antiseptic properties. Wash and clean the affected skin area, tap it fully dry, and then apply either apple cider vinegar or tea tree oil.
- Nail polish or nail polish remover can help get rid of fungal infections of skin around nails
- Take B complex vitamins as they help promote healthy skin and reduce risk to infections
- People who are at increased risk to developing fungal infections may use oregano oil, garlic oil, or other essential oils to protect skin from fungal growth
- Anti-inflammatory properties of fish oil can help decrease inflammation of hands caused by tinea manuum skin rash
- Fungus thrives in warm and moist environments. Hence ensure that hands are kept dry and cool
- Probiotics helps maintain the fine balance of skin surface flora
- Grapefruit seed extract has immune-system-boosting and antifungal properties. It can be used for treating tinea manuum fungal infection of the hands.