What is the function of basophils?
Basophils are a type of WBC or white blood cell granulocytes. They are the largest kind of WBC granulocytes but also the least common kind. They were discovered by German physician and Nobel Prize winner Paul Ehrlich in 1879. These WBCs are basophilic which means that they can be stained by basic dyes. Hence the name.
Basophils play a role in immune system inflammatory response and in the occurrence of chronic and acute allergic reactions such as asthma, anaphylaxis, hay fever, and atopic dermatitis, etc. They are capable of releasing serotonin and histamine that trigger inflammation; carrying out cell eating or phagocytosis; and secretion of heparin which hampers clotting of blood.
Basophils: Structure and Function
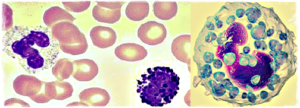
Basophils have big cytoplasmic granules which obstruct the nucleus under microscopic examination when stained. The nucleus is however clearly seen when unstained; it generally features 2 lobes. Basophils store histamine chemical which gets released upon stimulation of the cells. Basophils circulates in the blood stream and can be taken out of blood and used into a tissue when required.
Basophils form and get matured in the bone marrow. After activation, they get degranulated to produce proteoglycans, histamine, proteolytic enzymes, varied cytokines, and lipid mediators. All of them contribute to inflammatory reactions. Proteoglycans and histamine are pre-stored in granules of the cell, but other substances produced form newly. Interleukin-4 cytokine plays a very important role in IgE antibody production by the immune system as well as allergies formation.
Basophils occur during several types of inflammatory responses, especially those which result in allergic signs and symptoms. They have heparin anticoagulant which prevents quick clotting of blood as well as histamine vasodilator which enhances the flow of blood to tissues.
Basophils are associated with reactions to allergies as well as parasitic infections. They may be seen in abnormally high amounts at ectoparasite/ticks infection sites as well as in tissues affected by allergic reactions. They may sometimes add to the severity of the allergic response.
Protein receptors occur on the basophils cell surface. They bind an immunoglobulin called IgE antibody which is responsible for defense against macroparasite and allergies. Research has shown that T cells behavior may also be regulated by basophils and that the intensity of secondary immune reaction may be mediated by basophils.
Basophils: Normal range, high, low
It is possible to examine in vitro basophils degranulation via the use of flow cytometry and BAT or basophil-activation-test. BAT is very useful and provides accurate results in case of reactions to medications as well as diagnosis of underlying allergies.
As basophils form only around 0.5 to 1 percent of white blood cells circulating in the bloodstream, it is quite difficult to ascertain whether its count is low. Basopenia or low count of basophils has been known to have linkages with a chronic itching ailment known as autoimmune urticaria. Basophilia or high levels of basophils is also not that common. However, it has been reported to have links with certain forms of lymphoma or leukemia.
The percentage of different kinds of WBCs or white blood cells occurring in blood is measured by a blood differential test. The test also verifies the presence of immature or abnormal cells.
Acute stress or different kinds of infections can cause an increase in the count of WBCs. Increased white blood cells numbers may occur due to leukemia or other blood diseases or due to immune reaction inflammation. It may also be noted that abnormally higher levels of one type of WBC may result in a reduction in the levels of other kinds of white blood cells.
Some of the reasons for a reduction in basophils count are listed below:
- Cancer
- Acute infection
- Serious injury
A few reasons for an increase in basophils count are listed below:
- An allergic reaction
- Post splenectomy surgery
- Chronic myelogenous leukemia
- Myeloproliferative disease
- Collagen vascular disease
- Varicella infection
Blood test to check basophil count
Listed below are the steps taken to check basophils count via a blood test:
- Patients do not have to fast or prepare in a certain way to provide the blood sample. A needle with a syringe is inserted in the arm and blood specimen is collected.
- A drop of blood from the specimen will be taken by a lab specialist and then smeared onto a glass slide. A special dye is used to stain the smear so as to help find the different between different kinds of WBCs.
- Five different kinds of WBCs, i.e., basophils, neutrophils, monocytes, B and T cells lymphocytes, and eosinophils usually get detected in blood sample. The count of each kind of cell is counted by a technician or a special medical machine. Discrepancies in the number and/or proportion of the different types of cells with regards to each other will help determine the presence of any underlying condition.
- The blood test is not just used for diagnosis of diseases like leukemia, infection, or anemia, etc., but is also used for monitoring the effect of treatment.